Introduction
Gather the needed information:
- The chemistry needed for your experiment. For common metal etchants, check this website. Case studies on substituting with less toxic alternatives found here.
- Safety Data Sheets for each chemical. Download or open a new browser window for each SDS. Here is an alternative source for your SDS. Use an SDS that has Hazards and Toxicity information. Save the URL for each SDS that you use (Better: Save a PDF file of each SDS for later reference).
Make sure you download the Chemical Hygiene Plan below and open in Adobe Acrobat or Acrobat Reader. It is an interactive PDF and will not function properly in a browser.
Prior to submitting your Chemical Hygiene Plan to the Safety Facilitator, you will need to complete this guide and the following (Standard Operating Procedure).
-
-
Download the ChemicalHygienePlan (3 pages) using the link at the bottom of the Introduction.
-
Open this document in Adobe Acrobat
-
This document will not display properly in most web browsers.
-
-
-
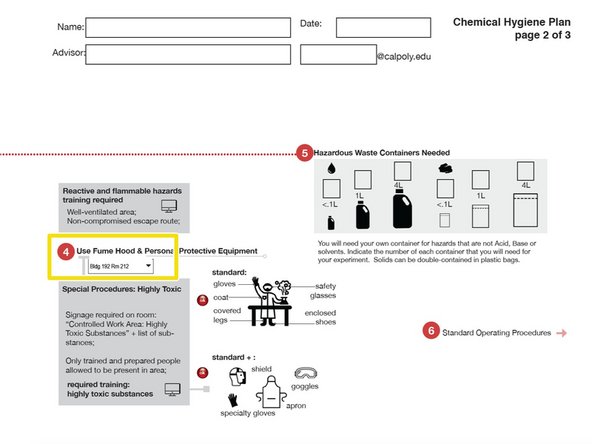
Enter name, date, Advisor and email address.
-
Describe purpose of the experiment.
-
Make sure you save your document; when there is too much text for the boxes, there will be a scroll bar to view the additional text in Acrobat.
-
-
-
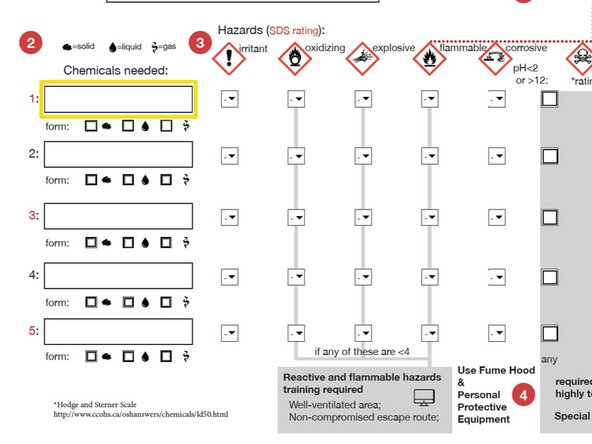
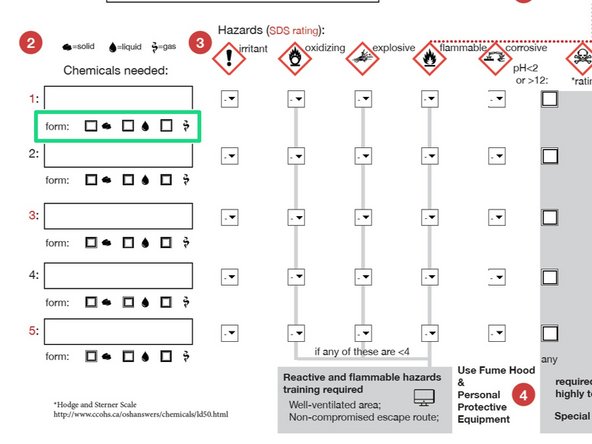
Enter each chemical needed.
-
Indicate the state (solid, liquid, gas)
-
-
-
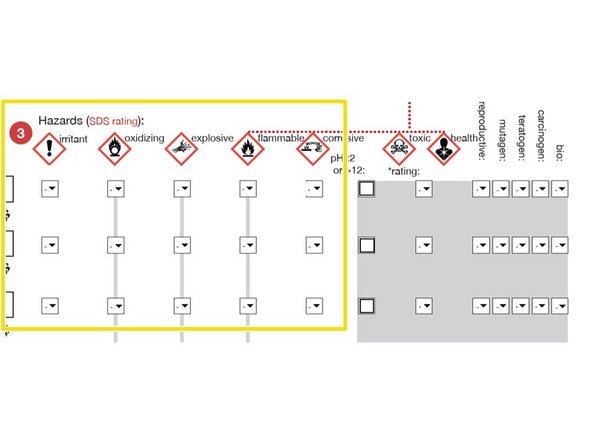
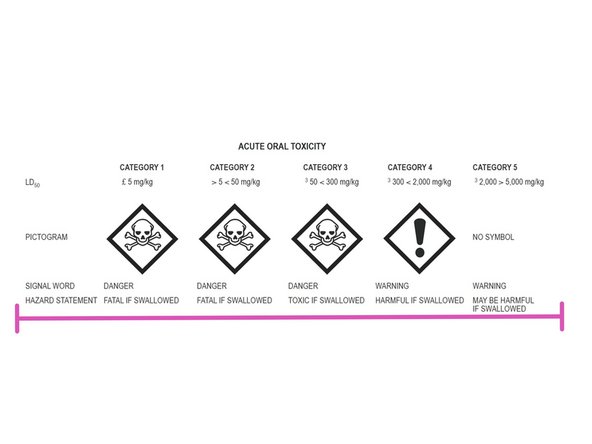
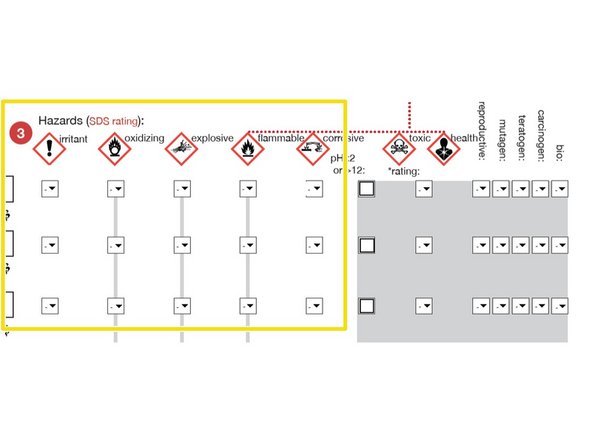
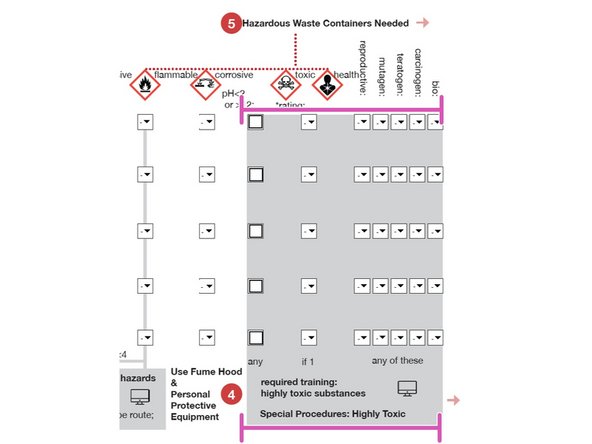
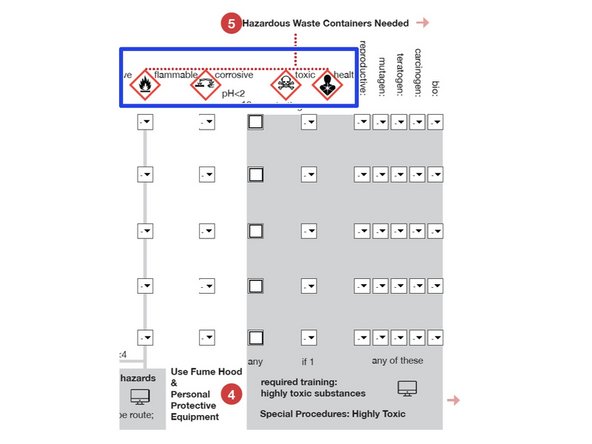
HAZARDS:For each chemical, use the Material Data Sheet and pulldown menu to indicate the hazard using the using the Hodge and Sterner Scale, Table 1 (scroll down).
-
The SDS may only include signal words.
-
If so, determine the HAZARD category (e.g. CORROSIVE) and select a number to match the description.
-
1=Extremely toxic; 5=Non-toxic
-
If "No information is available", indicate "2" as the hazard but be aware that it is "unknown."
-
-
-
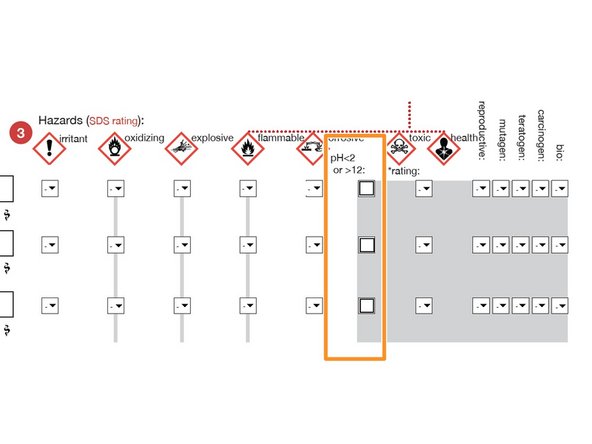
Check this box if any chemicals have a pH<2 or pH>12.
-
Are there less toxic alternatives? Search case studies here.
-
-
-
Toxicity for newer chemicals, such as nanomaterials, is unassessed/unknown. Err on the side of caution.
-
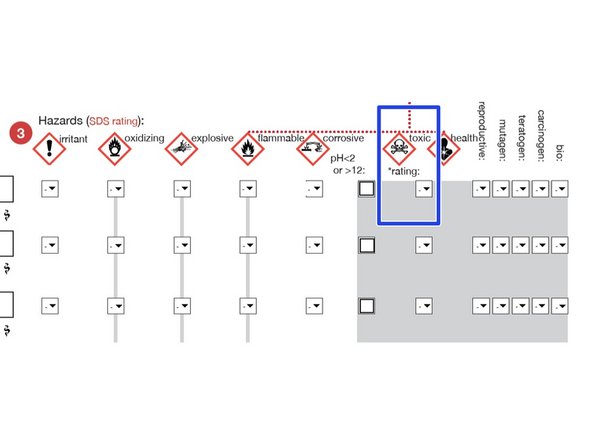
TOXICITY:For each chemical, use the Material Data Sheet and pulldown menu to indicate the hazard using the using the Hodge and Sterner Scale, Table 1 (scroll down).
-
If different routes of entry produce different toxicity levels, using the highest level.
-
e.g., Inhalation = 4, Skin = 1, Use "1" for toxicity
-
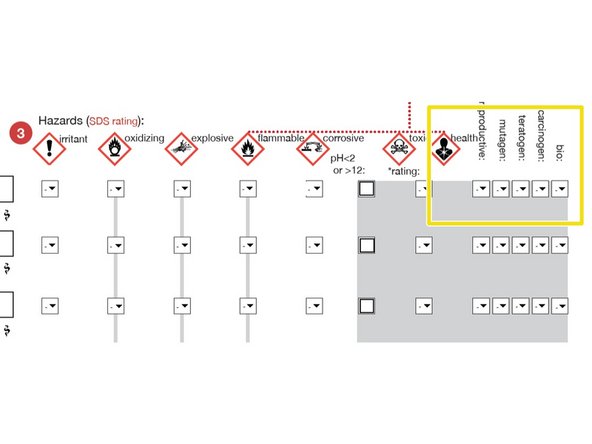
For Health toxins, if any of these categories is indicated on the SDS, use a rating of "1".
-
-
-
A "3" or less for any of these requires additional training.
-
Any of these conditions requires additional training for Highly Hazardous Substances
-
Fume hood is required for any doted item with a 3 or lower rating.
-
If SDS lists "No information found" or "Data not available," err on the side of caution and assign a "2".
-
-
-
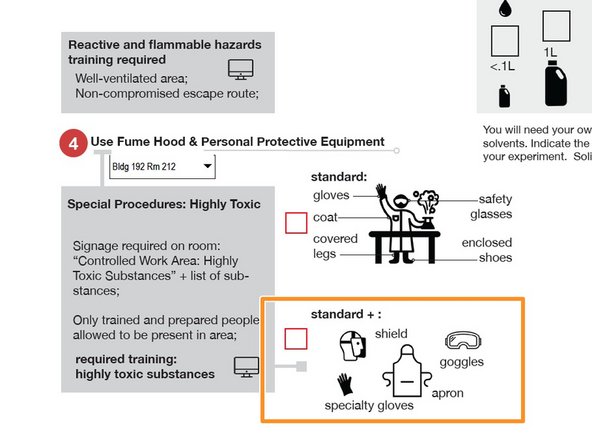
On page 2, indicate which fume hood location you will be using with the pull-down box.
-
192-212 and 41-203 have built in hazardous waste receptacles for ACIDS, BASES, SOLVENTS.
-
-
-
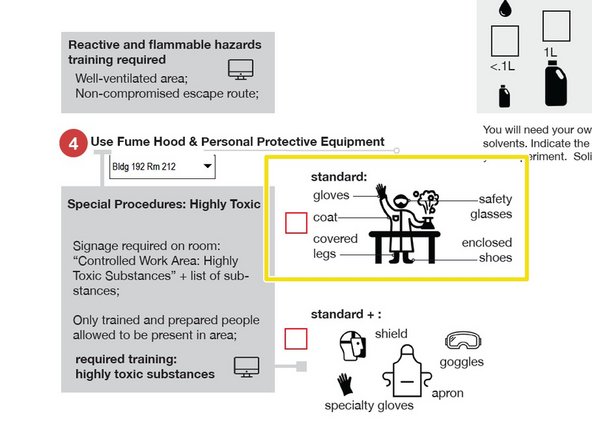
Check "standard" or "standard +"
-
"Standard +" Personal Protective Equipment is required for working with Highly Toxic Substances.
-
-
-
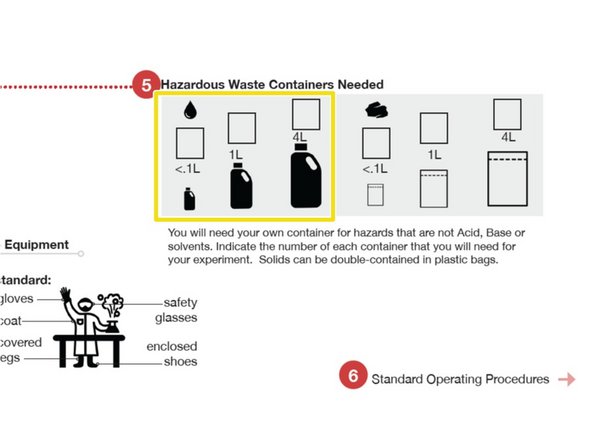
Indicate the approximate volume and number of Hazardous Waste containers for liquids
-
If you are generating standard Acid, Base, or Solvent waste, you do not need separate Haz Waste receptacles; Acid, Base, and Solvent Haz Waste can be found beneath the fume hoods.
-
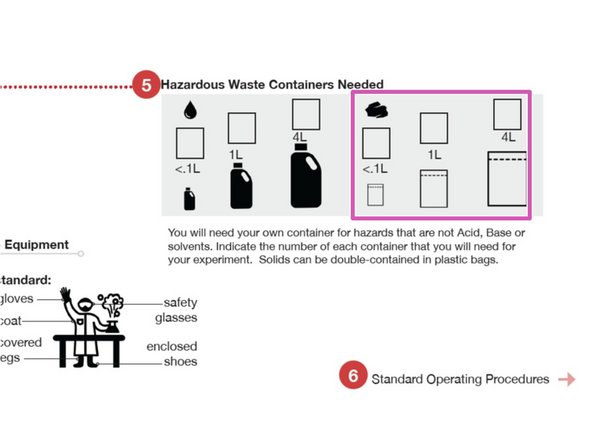
Indicate the approximate volume and number for solids Hazardous Waste.
-
An example of a solid Hazardous Waste would be filter paper or a plastic tray that was used to weigh a hazardous solid.
-
-
-
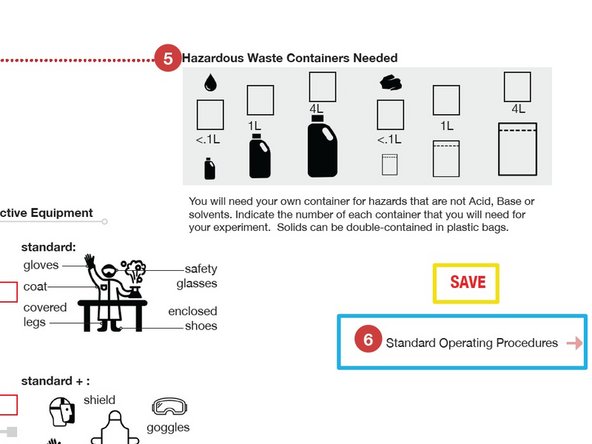
Save form.
-
You will need to submit the electronic version after it is approved.
-
You are now ready to create your Standard Operating Procedure (SOP), page 3.
-
You are now ready to move on to B2-How to create a Standard Operating Procedure.
You are now ready to move on to B2-How to create a Standard Operating Procedure.
Cancel: I did not complete this guide.
35 other people completed this guide.